The pitfalls of in-house procurement analytics tools
Whether you're swimming in millions of Excel rows or constantly questioning your data in PowerBI, in-house tools like these are far too common for Procurement teams. For all their flexibility and customizability, the impact on your team's potential far outweighs the perks of Do-it-Yourself analytics. Here, we'll describe why it's so hard to get in-house solutions to work.
Get ReportUpdated: Jun 10, 2025
In the fast-paced world of procurement, the allure of DIY analytics solutions like Excel, PowerBI, or Tableau is undeniable. They promise customization and control, allowing teams to build exactly what they believe they need. However, as many procurement leaders have discovered, the reality of managing these in-house solutions is far from ideal.
The complexity of procurement data landscapes can quickly overwhelm even the most robust internal teams. With data scattered across multiple ERP systems, external market subscriptions, and siloed internal sources, achieving a unified view for strategic decision-making becomes a daunting task. The manual effort required to cleanse and validate data is immense, often leading to inaccuracies that undermine trust in the analytics outputs. This not only strains resources but also increases the risk of human error, delaying processes and reducing organizational efficiency.
In this article, we'll dive deep into what procurement analytics is, the challenges of building a solution in-house, and a way forward for more advanced analytics.
The Importance of Procurement Analytics
In simple terms, procurement analytics is the process of collecting and analyzing procurement data to describe, predict, and improve business performance through informed decision-making. It involves collecting, classifying, and analyzing procurement data from multiple sources like ERPs and other systems. We at Sievo view procurement analytics as the process of turning procurement data into reliable automated insights and bottom-line impact.

With the ever-growing procurement mandate, the ability to leverage data effectively has become a cornerstone for achieving a competitive advantage with a sustainable, resilient, and diverse supply chain. Procurement analytics is not just a tool but a strategic enabler that transforms procurement from a cost center into a value driver.
The Hackett Group's Procurement Key Issue survey found that “data and analytics reporting” is the #1 improvement initiative for procurement teams, with 75% of respondents already pursuing an initiative. The capability to gain actionable insights from procurement data is vital to unlocking the full value potential of supply-side commercial opportunities and fully supporting the requirements of business stakeholders.
The companies we talk to usually have one thing in common: they struggle to aggregate and manage the data coming from different ERPs, data lakes, and third-party sources - and struggle even more with making insights easily accessible to the entire team. Whether they go with a procurement analytics provider like us or choose to build a solution in-house, the goal is the same: turning data into actionable insights, and doing so very quickly.
The Benefits
Companies utilize analytics solutions to try to free up time and focus for strategic decision-making and relationship management. Typically, traditional manual data analysis (like that in Excel) can take up tons of time for procurement managers. To stay competitive, there’s a dire need to automate processes to manage strategic procurement initiatives and identify both risks and opportunities while keeping operations on track.
When done right, procurement analytics provides a breadth of information to guide resource management, strategic planning, market research, and business development. There is a wide array of opportunities analytics can support:
- Cost Optimization: One of the primary objectives of procurement analytics is to identify cost-saving opportunities. By analyzing spend data and benchmarking against industry standards, organizations can uncover areas for cost reductions, such as consolidating suppliers or renegotiating contracts. By integrating spend data with market benchmarks, companies can negotiate better terms and reduce costs.
- Improved Decision-Making: Procurement analytics provides timely, accurate, and actionable insights that empower procurement leaders to make informed decisions. By analyzing historical data and predicting future trends, organizations can proactively manage risks and identify opportunities for cost savings and process improvements. With procurement analytics, decisions are made based on real-time, reliable data.
- Risk Mitigation: Procurement analytics helps organizations identify potential risks within the supply chain, such as supplier disruptions, regulatory compliance, or market volatility. By proactively managing these risks, organizations can ensure supply continuity and avoid costly disruptions.
- Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Organizations use procurement analytics to assess the sustainability and CSR impact of their procurement decisions and adhere to regulatory compliance. By analyzing supply chain data, like Scope 3 emissions, organizations can identify opportunities for more sustainable practices and meet commitments.
- Enhanced Supplier Relationships: With procurement analytics, organizations can monitor supplier performance, assess risks, and ensure compliance with contractual terms. This fosters stronger supplier relationships and enables organizations to negotiate better terms and conditions, ultimately driving value for both parties. Procurement analytics shines a light on supplier performance, allowing organizations to foster stronger relationships.
From Marketing to Finance, Sustainability to R&D, everyone can benefit from procurement data and its broad range of insights. For instance, procurement analytics can provide benchmarks and industry intelligence on which to base supplier negotiations. Insights on spend trends, changes, and growth in sub-categories can be eye-opening for other functions. With accurate data on hand, Procurement teams can facilitate better collaboration, sparking innovative relationships between suppliers and R&D.
Procurement analytics puts procurement in the driver’s seat, increasing its strategic contribution across the board. However, depending on your technical setup, getting quick, accurate, and actionable insights from your data is not a walk in the park.
Challenges of Procurement Analytics
The responsibilities of Procurement teams have expanded significantly. These teams are now expected to contribute to managing supply chain risks while maintaining continuity, facilitating digital initiatives with less-than-ideal data, and supporting ESG goals without compromising costs.
With this ever-expanding mandate, teams need to do more with less. The Hackett Group found that the procurement workload is predicted to increase by 8.0% but with little increase in headcount and operating budget.
Large enterprises truly are swimming in data, which puts a big burden on teams to handle these shifting mandates. Companies operate multiple ERP systems and external data sources. They’re struggling to keep up with the data overload and lack a single source of truth on spending patterns.
To better understand the multitude of challenges associated with enterprise procurement analytics, let’s look at several challenges and their root cause and long-term impacts.
|
Challenge |
Root Cause |
Effect |
|
Complex Data Landscapes |
Procurement departments often deal with a multitude of data sources, including multiple ERP systems, external market data subscriptions, global business entities, and scattered public data. This complexity is exacerbated by mergers, acquisitions, various regional currencies and languages, and decentralized operations, which lead to disparate systems and inconsistent data structures.
|
The fragmented nature of data landscapes makes it difficult to achieve a unified view of procurement activities. This lack of cohesion results in inefficiencies and hinders strategic decision-making. Organizations struggle to extract meaningful insights from their data, leading to missed opportunities and suboptimal procurement strategies. |
|
Incorrect and manual spend classification |
Poor spend classification often stems from incorrect and manual data entry errors, incomplete data, inconsistent data formats across systems, and a lack of standardized data governance practices. Messy and duplicated supplier data is caused by several factors, including decentralized procurement systems and varying naming conventions across different departments. These issues often arise in organizations that operate multiple ERP systems without a harmonized taxonomy, leading to inconsistencies and duplication in supplier records. Additionally, when organizations grow through mergers and acquisitions, they inherit diverse data systems that can further complicate data management and increase the likelihood of messy data. |
Inaccurate spend classification can lead to bad reporting and analysis, which undermines trust in analytics outputs and decision-making. When procurement teams rely on faulty data to guide their decisions, the risk of making erroneous decisions increases significantly. These inaccuracies may cause difficulties in tracking savings and managing supplier relationships, ultimately affecting the organization's bottom line. Decisions based on inaccurate data can have far-reaching consequences, such as selecting the wrong suppliers, misallocating resources, or misjudging market trends. This can result in financial losses, damaged supplier relationships, and reduced credibility with stakeholders. This impacts all departments of an organization. Over time, consistent reliance on inaccurate data can erode trust in procurement analytics and hinder the organization's ability to achieve strategic goals. |
|
Manual Work Needed to Improve Data Quality |
Many organizations rely on manual processes to address data quality issues, such as data cleansing and validation. Semi-frequent efforts to cleanse data with data consultants don’t address the root problem. This is often due to the lack of automated tools and technologies that can handle these tasks efficiently and upkeep data quality. |
The high manual workload needed to cleanse and validate data delays procurement processes and reduces the overall efficiency of the organization. This not only strains resources but also increases the risk of human error. This labor-intensive process can slow down procurement cycles and limit the ability to respond quickly to market changes or internal demands. It also diverts resources from more strategic activities that could add greater value to the organization. |
|
No single source of truth |
A complex data landscape and poor data quality impede the ability of procurement teams to access reliable and comprehensive data. Without a unified view of data, organizations struggle to leverage data-driven insights for strategic decision-making. Manual data processes further contribute to this issue by consuming time that could otherwise be spent on analysis and strategy. Likewise, financial and sustainability reporting becomes exceedingly time-consuming. |
The lack of data-driven decision-making based on a single source of truth results in missed opportunities for efficiency improvements and cost savings. Organizations remain reactive instead of proactive, unable to forecast trends or anticipate market shifts. Over time, this can lead to a competitive disadvantage as more data-savvy organizations capitalize on data insights to optimize procurement processes and supplier relationships. |
|
Unable to Find Opportunities Within Data |
The inability to identify opportunities within data often results from the limitations of existing analytics tools and the lack of advanced analytical capabilities. Basic tools like spreadsheets or BI reports may not provide the depth of analysis needed to uncover hidden insights. When insights are uncovered, users often do not trust the opportunity due to poor data accuracy. Often, the status quo with traditional tools slows down innovation. |
Organizations miss out on potential savings and efficiency improvements because they cannot fully leverage their data for strategic advantage. This limitation hampers the ability to optimize spend, negotiate better contracts, and implement effective risk management strategies. |
|
Low Adoption of Analytics Solutions |
Low adoption of procurement analytics solutions can be attributed to poor user experience, lack of training, and tools that do not align with user needs. If the tools are seen as difficult to use or irrelevant, users are unlikely to engage with them. |
Low adoption rates mean that the potential benefits of analytics tools are not realized. This results in a failure to improve procurement processes, reduce costs, or enhance decision-making capabilities. It also represents a poor return on investment for the organization and continued losses in upkeep for a tool almost no one is using. |
|
Hidden Costs to Maintain, Scale, and Update Solutions |
In-house analytics solutions often incur hidden costs related to maintenance, scaling, and updating. These costs arise from the need for ongoing IT support, software updates, and integration efforts, which are frequently underestimated during initial planning. |
Organizations face financial strain and resource allocation challenges as unexpected costs arise. This unpredictability can disrupt budgeting and planning, leading to inefficiencies and potentially jeopardizing other strategic initiatives. Reliance on internal IT teams can delay necessary updates and improvements, leaving the organization vulnerable to technological obsolescence. |
|
Wasting Money and Human Resources on In-House Tools |
In-house procurement analytics tools, such as Excel or basic BI tools, often require significant manual effort to maintain and update. These tools may not scale effectively with the organization’s growing data needs, leading to hidden costs and inefficiencies. |
Investing in maintaining in-house tools that are not effectively used or fail to solve procurement challenges leads to wasted financial and human resources. This diverts resources away from more strategic initiatives and inhibits the organization's ability to meet its targets. Over time, the inability to scale and adapt these tools can result in obsolescence, necessitating further investment in new solutions or technologies. |
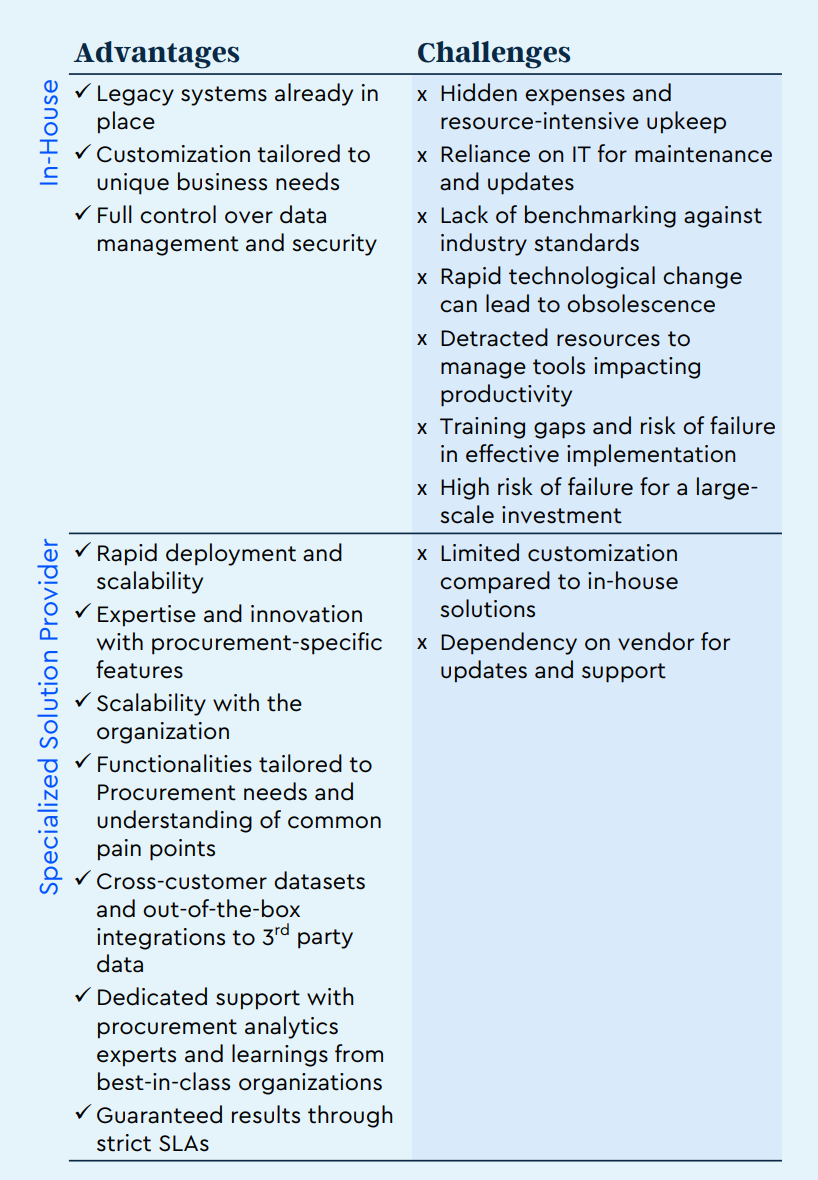
The advantages and disadvantages of in-house procurement analytics
Building an in-house procurement analytics tool involves the development of a custom system tailored to the specific needs and processes of an organization. This approach offers the potential for greater control over data and functionality but also presents significant challenges.
But, the hidden costs of maintaining and scaling DIY solutions can cripple budgets. Continuous IT support, software updates, and integration efforts are often underestimated, leading to financial strains and resource allocation challenges. The lack of advanced analytical capabilities in basic tools like spreadsheets can prevent organizations from uncovering hidden insights and opportunities, ultimately affecting their bottom lines.

As procurement responsibilities expand to include managing supply chain risks and supporting ESG goals, the need for agile, reliable, and insightful procurement analytics becomes critical.
Implementing procurement analytics requires alignment between Procurement and IT. It’s necessary to consider how the analytics tool will meet the diverse needs of the organization and support strategic objectives. Early involvement of stakeholders is crucial for successful implementation and adoption, as it fosters a shared understanding of goals and expectations.
But, if you're still willing to try developing in-house analytics tools for Procurement, here's (in our experience) the most common requirements and honest advantages and challenges.
Required Resources and Skills ✅
- Technical Skills: Developers proficient in programming languages, database management, and BI tools. Organizations often use Business Intelligence (BI) tools like PowerBI or Tableau, combined with data processing languages like SQL, Python, or R. The infrastructure may include databases (e.g., SQL Server, Oracle), data lakes, and cloud platforms like AWS or Azure for storage and computing power.
- Domain Expertise: Procurement specialists who understand the process and data requirements and are available to be consulted throughout the solution development to align with the needs of procurement.
- Procurement and Data Analysts: To interpret data insights and apply them to procurement strategies, i.e., end users who will understand the tool and gain value from it.
- Project Management: Strong leadership to oversee the project from initiation to implementation, often lead by a Center of Excellence or Procurement Transformation team.
- IT Infrastructure: Robust IT support to maintain and update the system, ensuring data security and compliance.
- Large financial commitment: taking on an in-house development project can take years. This requires a long-term financial commitment to the staffing and consultation required to see a project of this size through.
Advantages 👍
- Legacy: Large organizations typically have an in-house BI tool in place that they have invested a lot in. Applying these systems to procurement analytics could be seen as more efficient, but only because of past investment in the setup.
- Customization: Tailored to meet unique business requirements and integrate seamlessly with existing business tools (such as PowerBI with Outlook or Tableau with Slack).
- Control: Full control over data management, system updates, and feature development.
- Security: Potentially enhanced data security, as data does not leave the organization’s environment.
Challenges ❌
- Hidden Expenses: DIY solutions often incur unforeseen costs throughout their lifecycle, including maintenance, scaling, and updates.
- Reliance on IT: Continuous dependence on IT for tool maintenance and data interaction can lead to resource strain. Procurement often isn't the top priority for IT departments, which can lead to insufficient support and delayed responses.
- Resource-Intensive Upkeep: Regular updates, bug fixes, and scaling require significant resources. Manual data classification and cleansing are particularly challenging without automation. It's not just about integrating and connecting data to a BI tool; effective data cleansing is crucial but very difficult to manage manually.
- Lack of Benchmarking: In-house solutions limit access to external data, preventing benchmarking against industry standards and hindering innovation. Without insights from other organizations, there's less opportunity to learn and adapt based on broader industry trends.
- Rapid Technological Change: As technology and business needs evolve, there's a risk that an in-house solution will quickly become outdated.
- Impact on Productivity: Diverting resources to manage an in-house tool can detract from core business activities, impacting overall productivity.
- Training Gaps: While training materials may exist for BI tools, they often focus on general data visualization rather than specialized procurement analytics. Internal resources for training and adoption need to be developed from scratch, with no guarantee of success.
- Risk of failure: Failure to implement effective analytics can jeopardize the position of procurement COE leaders. Relying on IT, which may lack specific experience, poses a risk compared to partnering with experts like Sievo.
Organizations must weigh these factors carefully when deciding whether to build an in-house solution or opt for a third-party procurement analytics solution. The decision often hinges on available resources, the complexity of requirements, and long-term strategic goals.
To compare this to what best-of-breed solutions offer, here's a summary of the key differences:
To learn more, read our full guide to compare Sievo and in-house procurement analytics tools!
Conclusion
All these challenges have led many companies to consider what to do next. The procurement analytics market is large, with multiple solution areas and tools out there. As organizations seek more specialized providers, they should also consider how all solutions will interact. For some, outsourcing analytics is not considered customizable enough to meet their unique needs, but this can be a trap. Many global enterprises face the same challenges, and solutions like Sievo are here to help.
Sieve offers a comprehensive, scalable, and secure platform tailored to meet the unique needs of procurement teams. By switching to Sievo, organizations can free up resources, reduce operational burdens, and transform procurement from a cost center into a strategic value driver. Don't let the pitfalls of DIY solutions hold your team back—embrace the future of procurement analytics with Sievo. Watch this short video to see how:
Learn why you should make the switch to Sievo.
In this essential guide, we delve into the intricacies of procurement analytics, providing a clear comparison between in-house solutions and specialized BoB software like Sievo.