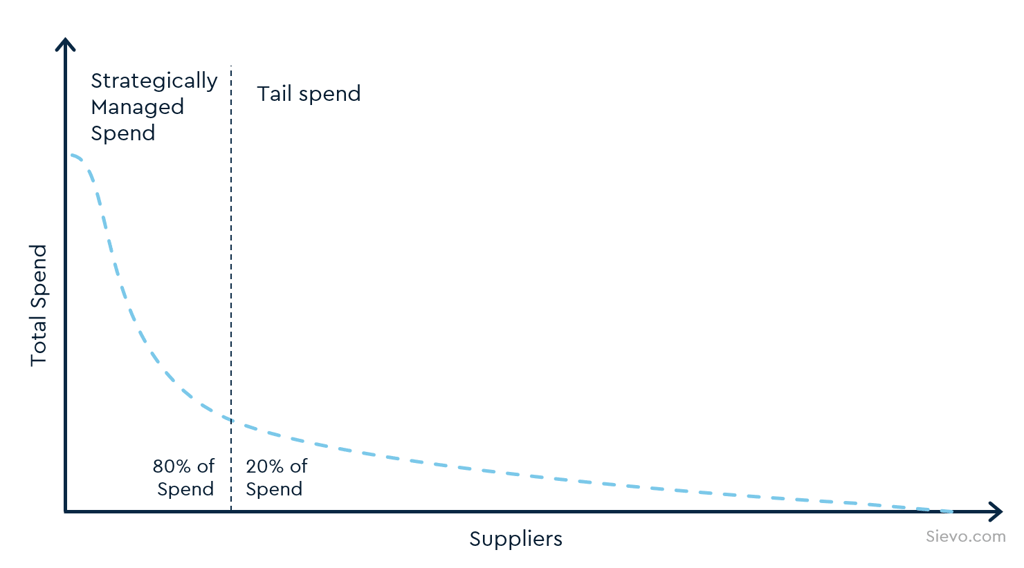
Tail spend refers to the portion of an organization’s procurement that accounts for approximately 80% of transactions but only 20% of total spend.
Though often overlooked, managing tail spend effectively can unlock substantial savings and operational efficiency.
According to a 2024 Boston Consulting Group study, organizations can realize 5% to 10% cost savings by actively managing tail spend.
This guide will help you:
-
Understand what tail spend is
-
Identify key challenges in managing it
-
Explore the benefits of a tail spend program
-
Learn a 5-step process to manage it
What is Tail Spend?
Tail spend includes a high volume of low-value purchases that are often indirect, non-core, and spread across many suppliers.
These purchases are essential but can fly under the radar of procurement teams focused on strategic sourcing.
Common characteristics of tail spend:
What Exactly is it Made Up Of?
Every procurement team will have a different perspective on what a spend tail is. What it constitutes in one organization or within one spend category may be different from another.
It can include:
-
Spot or one-off purchases
-
Maverick or “rogue” purchases outside contracts
-
Purchasing card buys and petty cash items
-
E-catalogue spend
-
Any other low-value purchases that bypass procurement processes
Want to understand spend categories better? Check out Spend Analysis 101.
Challenges in Managing Tail Spend
By its nature, spend is complicated. The effort and time required to manage high volumes of data, combined with the lack of strategic importance in the tail, can make it a low priority for procurement teams, despite the opportunities it presents.
-
Poor data visibility: Disparate systems, inconsistent data, and decentralized purchasing
-
Low strategic priority: Focus is typically on larger, high-value categories
-
Time and resource intensive: Managing high transaction volumes requires effort
These factors make tail spend appear less valuable, even though it holds hidden opportunities.
Benefits of a tail spend management program
With accurate spend classification in place, you can begin to tackle tail spend more systematically and analytically.
A strong tail management strategy can provide a competitive advantage for an organization. Some of your biggest cost and time savings can come from your smallest purchases.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Reducing the number of suppliers and introducing automation simplifies procurement and cuts down on time-consuming tasks.
-
Supplier consolidation: Fewer vendors and contracts to manage.
-
Automation through e-catalogs: Speeds up purchasing and reduces manual steps.
-
Self-service procurement: Enables compliant buying without procurement involvement.
Reduced Supplier Risk
Improved oversight of tail spend reduces exposure to non-compliant purchases and supplier fraud.
Organizations gain more control over their vendor base, leading to safer and more reliable procurement.
-
Fewer rogue purchases: Monitoring and guiding spend behavior reduces unauthorized buying.
-
Improved SLA and contract compliance: Enforcing preferred suppliers and processes strengthens policy adherence.
-
Lower fraud risk: Cleansing supplier data and removing duplicates or obsolete vendors limits vulnerabilities.
Improved Stakeholder Satisfaction
When procurement systems are transparent, intuitive, and efficient, users are more likely to adopt them.
-
Simplified guidelines: Rules are easier to follow.
-
Faster cycle times: Quicker approvals and transactions.
-
Higher productivity per employee: Less time on low-value tasks.
-
Enhanced data quality and reporting: More reliable insights.
How to Manage Tail Spend in 5 Steps?
Once you understand the scope and scale of your tail spend, apply these steps for better control:
-
Identify your tail spend
Decide what tail spend means in your organization. Only then can you take the appropriate steps to effectively manage and optimize it.
If the idea seems too daunting, you could make a start by understanding what it is in one division or department where there are obvious issues.
-
Streamline internal processes
It is vital to have clear procurement processes and ensure they are properly communicated and enforced. Involving stakeholders throughout the process of identifying target areas and managing the tail provides continuing support.
End-user enthusiasm may be low for such improvement projects if the reasons for managing the tail are not explained and the benefits for them are not visible.
-
Organize the data
Once you have decided on the scope and identified the business systems and sources that store the data, the next step is organizing the actual data.
Cleansing, classifying, and analyzing spend data will lead to greater spend awareness on which informed business decisions can be made. Cleansing includes standardization of field formats such as dates and currencies and normalizing supplier names.
New and innovative digital software solutions that extract, analyze, and track your spend provide support for this step.
-
Actually use the insights
Reports resulting from a formal analysis process can provide both numerical and visual representations of the information in a dashboard format.
Using suitable software tools, output reports are customizable, providing insights into consolidation and cost-saving opportunities e.g., industry sector, division or location, and by commodity. Now execute!
-
Monitor the benefits
Monitoring the success of your tail spend management program requires deciding on key performance indicators (KPIs) and suitable review periods. Examples of KPIs are:
-
Cost savings achieved against a pre-agreed benchmark or savings targets
-
Productivity improvements – actual time saved per activity, reduction in the number of quotes requested, % of tail spend through e-catalogs, % reduction in the number of non-contracted suppliers
-
% of spend under strategic management vs unmanaged
Don't Tackle Tail Spend Alone
Tail spend management requires time, expertise, and resources. Consider:
-
Dedicated internal teams with KPIs and goals
-
Technology and automation tools for classification and tracking
-
External experts to accelerate implementation and results
Many organizations see the best results when they blend in-house capabilities with external solutions, especially for data analysis and AI-driven spend management.
“Sievo delivers value we've never experienced before. We see so many opportunities we previously missed that are just ripe for picking. It's as simple as looking at Sievo.”
Angel Simenov, MediaMarktSaturn
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is tail spend in procurement?
Tail spend refers to the portion of an organization's purchases that make up about 80% of transactions but only cover 20% of total spend. These are often low-value, indirect, or one-off purchases that are essential but not strategically managed.
Why is tail spend often ignored by procurement teams?
Tail spend is typically overlooked because it involves many small transactions that are complex to track and manage. The lack of data visibility and the lower strategic importance compared to core spend categories make it a lower priority.
What challenges do organizations face when managing tail spend?
The main challenge is limited data visibility caused by multiple systems, siloed departments, poor supplier data, and decentralized purchasing. This complexity makes tail spend management difficult and time-consuming.
How can managing tail spend benefit an organization?
Effective tail spend management can lead to cost savings, improved efficiency, reduced supplier risk, and better stakeholder satisfaction. It can also enhance data quality, compliance, and productivity.
What are the key steps to manage tail spend effectively?
Successful management involves identifying your tail spend, streamlining processes, organizing data, using insights from analysis, and monitoring results with clear KPIs. Each step helps bring more control and visibility to this spend category.
What tools can help with tail spend management?
Digital software and analytics tools can extract, cleanse, and analyze spend data. They support monitoring, reporting, and strategic decision-making, making tail spend management more efficient.
Is it better to manage tail spend in-house or seek external help?
Organizations should assess their capability and resources before deciding. While some work can be done internally, leveraging experts and automation technology often yields the best results.