A Request of Quotation (RFQ) is a competitive bid document used when inviting suppliers or contractors to submit a price bid for products or services where the requirements are standardized or produced in repetitive quantities.
An RFQ is often used for high-volume/low-value items and should be completed more quickly than an RFP (Request for Proposal). The buyer must provide a technical specification as well as his commercial requirements. The document may sometimes be called an Invitation to Bid or Invitation to Tender.
In this article, we'll explain the RFQ process in 6 simple steps.
The RFQ Process in 6 steps
While requests for quotes come in all shapes and sizes, they generally follow six key steps. Let's review the process from the point of view of a game of snakes and ladders.
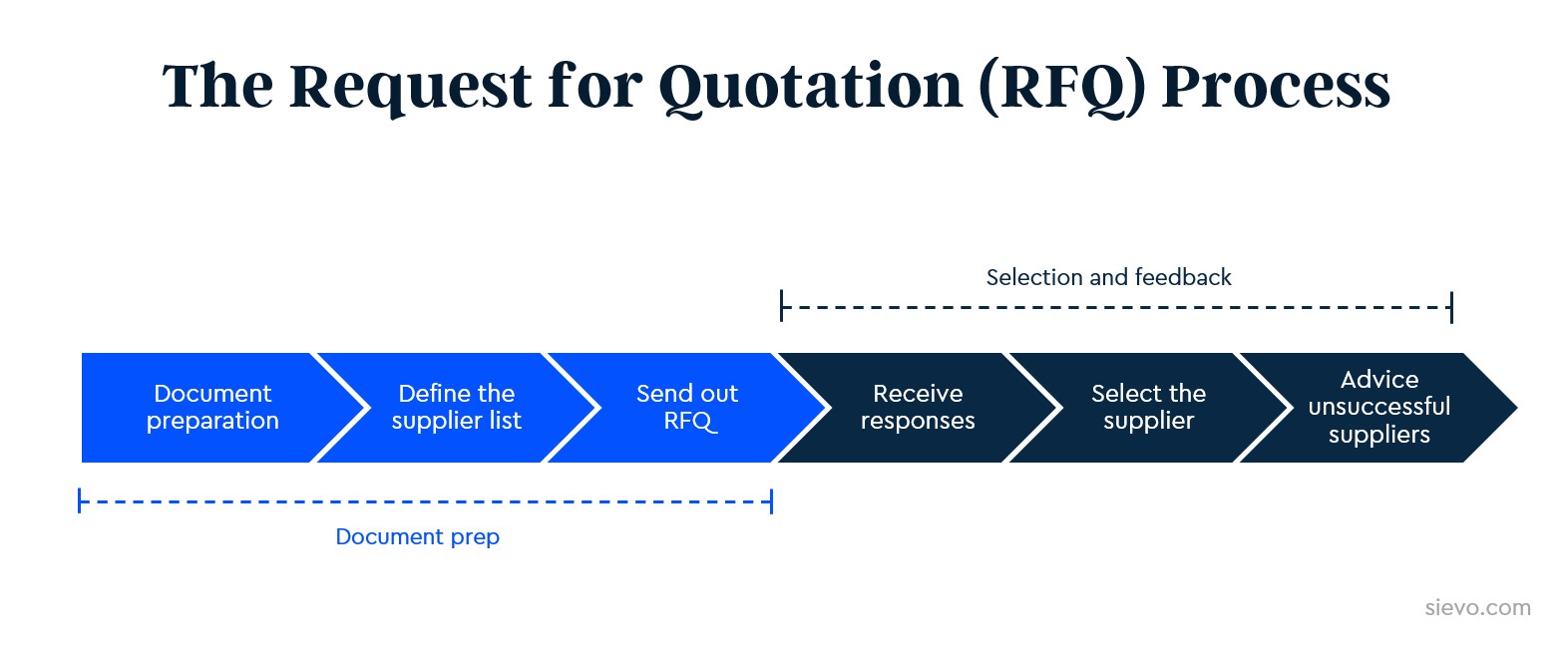
1. Preparation of the document
A well-constructed RFQ should open with an introduction to the company and its business and a need statement. It then allows suppliers to express their offers clearly to fulfill that need and provides the buyer with a fair way to select the best solution.
An efficient way to do this is to provide bidders with a template designed to elicit the complete information required in a format that allows for easy comparison. Time spent in preparation will save time and frustration later.
Start your RFQ by preparing the relevant documentation. Identify clear requirements with input from internal stakeholders to make sure you’ve included all the requirements, which are at least these:
- Definition of the products or services required with detailed specifications
- Delivery requirements
- Quantities
- Payment terms
- The proposed method of evaluation
- Decision timeline and review process
- Contract terms and conditions
- Submission requirements
The template, in a format that can easily be compared, such as Excel, should include quantities, cost breakdown, if applicable, pricing, volume discounts, and total price (before taxes).
Example of an RFQ Pricing Template
2. Define the supplier list
The RFQ could be open to all possible bidders. The global market is dynamic, and there are always new entrants. To streamline the process, it may be necessary to run a pre-selection event before sending your RFQ to a closed list of approved bidders. This is the point at which you need to assess both financial and operational risks.
3. Send out RFQ
The RFQ must include clear instructions for its completion and submission due date. It is important to allow enough time for a bidder to formulate his response. The RFQ should include, as an attachment, the buyer’s terms and conditions. During the bid preparation period, there must be a method by which any potential supplier can ask clarification questions and receive answers. All bidders should be provided with the same information.
Many service providers with hosted solutions and e-sourcing software can automate some parts of the process, including the Q&A and sharing the answers. Bidders can upload their offers with the required supporting documents and receive notifications.
4. Receive responses and analyze results
Whether received from an automated system or manually, bids must be subject to confidentiality to ensure a fair result.
Best practice: close the bidding on the due date and open all bids immediately after that.
5. Select the successful supplier
The evaluation process is easier and faster if an efficient, well-thought-out template is used. The successful bidder will be the one offering the lowest price for the goods or services specified while complying with all selection criteria. A clarification process may be necessary, and minor negotiations are needed to reach the correct result. The deal is only completed when the contract is signed.
Best practice: Document all the actions that were taken during the RFQ process, including the number of bids sent out, the number of bids received, the evaluation criteria, the bid evaluation committee members, and the final decision.
6. Advise unsuccessful suppliers
Notify the other bidders that the contract has been awarded. Thank them for their participation; you may need them again at a future date.
Final thoughts
The 6 steps above are traditionally followed in the commercial sector of the economy. Government departments and other public authorities may have more stringent rules for their RFQ process.
The RFQ process can become subject to irregularities if the list of bidders is manipulated or unnaturally restricted to limit the competition.
The process also has the potential to be abused as requirements can be broken down into smaller parcels to avoid a more lengthy and complex RFP process. Don’t let that happen to you.
However, in most cases, this 6-step RFQ process should meet your needs.