AI in Procurement
The Ultimate Guide for Procurement Executives - including Definitions, Examples and Best Practices.
Want to learn how procurement pros use AI to make better decisions, faster?
CLAIM YOUR FREE AI EBOOK
Updated: Feb 2, 2026
AI in procurement is often positioned as a cure-all for complex business problems.
In reality, most procurement teams want something simpler: better data, faster decisions, and less manual work.
But what are the real AI opportunities in procurement? How can artificial intelligence in procurement help solve today’s biggest challenges? What are the AI use cases in procurement that make day-to-day work easier?
This guide cuts through jargon to explain what AI procurement actually delivers in 2026, with clear definitions, concrete examples, and practical guidance.
AI Use Cases in Procurement
It's 2026: You already know that LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, or Copilot are great at taking long messages or spreadsheets and digesting them for you. The next step is to apply AI to procurement workflows such as spend analysis, supplier management, and decision support.
Below are practical, proven ways teams are using AI in procurement today:
Identify More Savings Opportunities, Faster
With AI-backed spend classification and continuous data enrichment, procurement teams can confidently act on insights without the burden of manual data processing.
-
Classify spend with higher accuracy – Procurement teams that work with AI tend to work with clean, structured data, improving classification accuracy and coverage across all spend categories.
-
Expand your savings scope – AI-powered insights uncover hidden cost-saving opportunities, even in tail spend, by analyzing internal and external data sources.
-
Detection opportunities around the clock – AI monitors procurement data 24/7, surfacing new savings possibilities in areas like working capital, cost reduction, supplier consolidation, and sustainability initiatives.
-
Actionable Insights – Instead of static reports, the right AI tool can deliver ready-to-act recommendations, helping procurement teams move from analysis to execution faster.
With AI-driven insights, procurement professionals can reduce manual effort, improve decision-making, and capture more savings opportunities, all while ensuring data accuracy and relevance.
Supplier Continuity and Risk Management with AI
AI enhances supply continuity by providing real-time visibility into supplier risks and market changes. By integrating internal procurement data with external sources, AI helps procurement teams proactively manage disruptions and maintain stable supplier relationships.
-
Comprehensive Supplier Intelligence – a decent AI tool consolidates internal, third-party, and industry-wide data to provide a 360° view of supplier performance, risk factors, and compliance metrics, ensuring procurement teams have the most accurate and up-to-date insights.
-
Detect risks proactively – AI can continuously monitor supplier signals, identifying potential disruptions such as financial instability, regulatory changes, or shifts in supplier ownership, allowing procurement teams to take preventive action before issues escalate.
With AI-driven supplier intelligence, procurement teams can mitigate risks, ensure supply continuity, and make informed sourcing decisions—all while maintaining a proactive approach to supplier management.
AI-Driven Supply Chain Intelligence
AI enhances supply chain visibility by harmonizing procurement data and integrating diverse information sources, enabling procurement teams to make more informed, strategic decisions.
-
Accurate, Harmonized Procurement Data – AI can deduplicate and standardize material data, ensuring procurement teams can compare prices, consolidate ERP records, and refine spend classification across global and local operations.
-
Comprehensive Supplier Insights – AI processes structured and unstructured data, providing a 360° view of suppliers, including risk factors, sustainability commitments, and payment term recommendations.
-
Integrated Sustainability and Risk Data – AI enriches procurement data with third-party and industry-wide insights, helping teams evaluate supplier diversity, ESG performance, and compliance risks in a single, actionable view.
With AI-powered supply chain intelligence, procurement professionals can improve data accuracy, enhance supplier evaluations, and ensure alignment with sustainability and compliance goals.
Types of AI in Procurement
From a Procurement perspective, any software solutions that include self-learning, and smart algorithms can be considered AI. You can see examples in later chapters of this guide and refer to these common definitions

-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Algorithms designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, making decisions, or solving problems using data.
-
Machine Learning (ML): Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn patterns from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each task.
-
Generative AI (GenAI): Generative AI describes AI systems that can create new content, such as text, images, or summaries, based on patterns learned from existing data.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Natural language processing is an AI field that enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
-
Agentic AI: Agentic AI is a more autonomous form of artificial intelligence designed to analyze data holistically, offer proactive recommendations, and even automate decision-making when appropriate. Read more about how Agentic AI is closing the Data-to-Action gap in procurement.
All forms of AI involve algorithms – sets of rules specifying how to solve a specific problem. Algorithms can be calculated by anyone gifted in math, but they also form the basis of most computer software. The work of algorithms in software is not visible to the human eye, but experts can program and reprogram them to solve problems important within software environments.
How AI Can Help in Procurement
AI thrives at solving complex problems involving large amounts of data but clearly defined measures of success. A study by Harvard Business Review and Deloitte explored the key areas where business executives expect to see the most success with AI. While each organization has its own challenges and opportunities, these can be the areas where AI can bring value to Procurement.
Key areas AI can support Procurement:
-
Make better decisions – artificial intelligence can provide timely analytics and data-driven insights to make better sourcing decisions.
-
Identify new opportunities – shifting through vast amounts of data, AI can uncover new savings or revenue opportunities.
-
Improve operations – artificial intelligence has the potential to streamline or align internal business operations, even in large organizations with many business units or geographic locations.
-
Automate manual tasks – AI can automate many time-consuming tasks, such as monthly processes, or Procurement performance reporting.
-
Free up time – by taking care of more routine tasks, AI can free up Procurement resources for more creative or strategic tasks like key supplier relationship management.
-
Capture or apply scarce knowledge – artificial intelligence can help Procurement organizations capture relevant new sources of data, for example, from external data sources like the Internet.
-
Identify new suppliers or markets – with access to vast amounts of external data, AI can help identify new suppliers or even new markets to enter.
-
Optimize supplier relationships – AI has the potential to make supplier relationship management more data-informed.
Automation in Procurement
Procurement automation means automating your procurement processes to maximize efficiency and reduce cycle time. Automation frees employees from repetitive, manual, and time-intensive tasks and speeds up the entire process.
Automation is a core outcome of AI for procurement, but not all automation requires AI. The most effective programs combine workflow automation, analytics, and artificial intelligence to improve efficiency at scale.

Automating the procurement cycle: 6-step approach
-
Map your current procurement process
-
Audit the current procurement process
-
Identify key areas for automation (labor-intensive, repetitive bottlenecks)
-
Choose the analytics solution that supports automation
-
Build automation workflows and approval points
-
Measure automation success and improve
Examples of Procurement AI
While the adoption of AI in business applications remains in its early stages, there are more examples of AI use within Procurement functions. Machine-learning algorithms are widely used in spend analysis to improve and speed up a range of processes, including automatic spend classification and vendor matching, and much more is on the horizon.
The most established procurement AI examples appear in data-intensive areas where accuracy, scale, and consistency matter.
Machine Learning in Spend Classification
Examples of spend classification techniques include:
-
Supervised Learning in Spend Classification – when humans train algorithms to detect patterns in spend, removing dull work of repetitive new spend classification.
-
Unsupervised Learning in Vendor Matching – when algorithms are programmed to detect new and interesting patterns in vendor relationships without intervention or support from humans. For example, if you have DHL, DHL Freight, Deutschland DHL, and DHL Express in your data, the machine learning algorithms are easily able to consolidate these together as DHL for increased visibility and data coherence.
-
Classification Reinforcement Learning – where spend classification actions taken by algorithms are reviewed by humans and rewarded or punished depending on the consequences.
The 80/20 of procurement AI
When building a business case for AI procurement, assume partial, not total, automation. In many cases:
-
~80% of spend classification can be automated
-
~20% requires human review and exception handling
This human-in-the-loop model delivers faster results while maintaining data quality and control.
Capturing Supplier and Market Data with AI
Use techniques such as natural language processing to look for and capture data on suppliers or specific markets. For example, tracking social media channels for signals about suppliers' risk positions. Better predictions such as price predictions, maintenance needs, and stock market forecasting can be improved by AI.
AI can be utilized to take advantage of new sources of data. So-called “external” data sources can include market indices, company credit ratings or publicly available information about suppliers. AI-powered methodologies can sift through immense amounts of external data to identify opportunities and provide benchmarks and recommendations for improving performance.
Let’s take, for example, the task of benchmarking your performance to those of others. Say, at the moment, you are mainly using internal data as well as a static historical data set to benchmark your performance. This way you may get a fairly accurate picture but are still missing out on some key observations. A whole new level of insight comes into play when external data, such as market reports and stock prices, enter the field.
Anomaly Detection
AI is increasingly used to detect anomalies, risks, and opportunities in procurement data as they emerge. As AI processes an ever-increasing amount of data, it is able to stay up-to-date on the latest developments and changes in the operating environment.
This will enable all anomalies and changes to be noted instantly and more accurately. AI will be able to immediately notify the team if something abnormal has occurred and can give instant suggestions on what could be done.
It can also be able to showcase possible simulations for different scenarios and new opportunities utilizing the data it has access to. The end result is that human procurement practitioners will be more aware of what is happening and will be able to take action sooner.
In addition, users can trust that the recommendations AI makes are based upon real facts rather than human hypotheses or guesswork. This gives the procurement leaders the confidence that their decisions are based upon real data, which removes uncertainty and leads to better decisions.
Why these examples matter
These examples show where AI use cases in procurement consistently deliver value:
-
High data volume
-
Repeatable decisions
-
Measurable outcomes
They also illustrate why the most successful procurement AI deployments combine automation with human oversight.
GenAI for Procurement
Generative AI is a broad class of AI characterized by the capability of generating text, images, or other media by learning patterns and structures based on input data. Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI's GPT are one of the most exciting developments in recent years.
As these models mature, GenAI has moved from experimentation to practical application. Procurement teams are using it to work faster with documents, communications, and unstructured data—areas that traditionally consume significant manual effort.
Wondering how Sievo integrates GenAI into its solutions? See here!🤖
Synthesizing unstructured data
GenAI can analyze text-based records such as supplier communications, meeting notes, contracts, and documents to:
-
Summarize discussions and interactions
-
Highlight key issues or risks
-
Generate structured insights from free text
This reduces manual review and improves information accessibility.
Capturing external data and making it usable
GenAI can scan and summarize external sources such as:
-
Supplier-specific news
-
Industry publications
-
Public web content
Relevant insights are delivered in a concise, usable format, helping procurement teams stay informed without continuous manual monitoring.
Generating briefs and text-based documents
GenAI can draft and summarize common procurement documents, including:
-
Supplier relationship summaries
-
Statements of Work (SOWs)
-
Requests for Proposal (RFPs)
-
Purchase order descriptions
These outputs accelerate preparation but should be reviewed before use in formal or contractual contexts.
Data classification and mapping
LLMs are effective at supporting procurement data processing tasks such as:
-
Spend and transaction classification
-
Supplier normalization
-
CO₂ and sustainability data mapping
-
Data engineering and transformation
GenAI complements traditional machine learning by handling complex or inconsistent text inputs.
Automated vendor communication
GenAI-powered chat interfaces can generate clear, context-aware supplier communications for tasks such as:
-
Requesting pricing or lead times
-
Collecting product or service information
-
Responding to routine supplier inquiries
This improves response speed while maintaining consistent messaging.
Risk Mitigation and Compliance
GenAI can analyze contracts and policy documents to:
-
Identify potential risks and non-standard clauses
-
Compare contractual terms with regulatory requirements
-
Surface changes that may affect compliance or supplier risk
These insights support risk monitoring but should remain part of a governed review process.
Read more about ChatGPT for Procurement and our view on the hype
Practical guidance on using GenAI in procurement
GenAI works best when used as a productivity and decision-support tool, not as a fully autonomous system. Outputs should be reviewed, validated, and governed—especially where compliance, financial commitments, or supplier obligations are involved.
Procurement AI Software
High-performing procurement organizations adopt AI earlier and more consistently. Research from Deloitte shows that top Chief Procurement Officers are significantly more likely to have fully deployed AI or cognitive capabilities across the procurement cycle.
In practice, procurement AI software embeds artificial intelligence into existing tools rather than replacing them. Below are the most common software categories in which AI in procurement delivers value today.


Contract Management Software
AI is widely used in contract management to extract, analyze, and monitor contractual information. One very concrete example is natural language processing, which enables software like Docusign Insights to automatically scan and interpret lengthy and verbose legal documents for potential savings opportunities.
Supplier Risk Management
Artificial intelligence can be used to monitor and identify potential risk positions across the supply chain. For example, in RiskMethods RiskIntelligence, big data methodologies are used to screen millions of data sources and generate alerts within supply chain risk management software.
AI in Purchasing Software
AI is increasingly embedded in purchasing and procure-to-pay tools to reduce manual review and improve compliance. For example, on Tradeshift's platform, a chatbot called Ada can check purchase status or automatically approve virtual card payments.
Accounts Payable Automation
Machine learning plays a central role in modern AP automation by improving accuracy and speed. Stampli is one example of AP automation software that uses machine learning to speed up payment workflows and detect fraud.
AI Spend Analysis Software
In procurement spend analysis, machine learning algorithms are widely used to improve and speed up a number of processes, including automatic spend classification and vendor matching. We'll go through this example in more detail in a separate chapter of this guide.
New Supplier Identification
Big data techniques enable new ways to identify, manage, and utilize supplier data across public and private databases. Platforms such as Tealbook use machine learning to enhance supplier discovery based on information gained, cleansed, and enriched from the Internet.
AI in Strategic Sourcing
Artificial intelligence can also be used to manage and automate sourcing events. Keelvar‘s sourcing automation software uses machine learning for the recognition of bid sheets and has specialized category-specific eSourcing bots, such as raw materials and maintenance/repair.
Supervised learning with Procurement Data
Most uses of artificial intelligence in business contexts require some human supervision. When you see implementations of AI in procurement, they are likely to involve supervised learning. In these cases, procurement experts are included to actively train machines to perform a specific task.
Here is how you could train AI with procurement data:
-
As a first step, a set of training data is given to an AI algorithm with a specific challenge. For example, it could be asked to analyze how 100,000 invoices have been classified into different spend categories.
-
With a clear goal and some training data in mind, you could then begin to give the AI algorithm unclassified Procurement data to classify based on the logic it has observed in the training data.
-
In cases where AI has high confidence it can classify data correctly, the data would be automatically categorized without human input.
-
In cases where AI does not have high confidence, the classification decisions would be reviewed by Procurement experts. This process is sometimes called “human annotation.”
-
-
With feedback from human reviews, Procurement Data would be both classified and utilized to actively teach the AI algorithm to classify future data.
-
Over time, the confidence of the AI would improve to automatically classify more data, while also increasing the quality of data classification based on the human input.
When you consider this training process from the point of view of a Procurement organization, consider what are the tasks at hand where you would have enough training data, a need to consistently process unclassified data, and a concrete output that adds business value.
Use of Machine Learning in Procurement
Machine learning in procurement is the application of self-learning, automated statistical methods to solve specific challenges or improve operational efficiency. With machine learning (ML), procurement can deliver the highest quality in relation to volume and bottom-line impact.
Machine learning is the subset of AI with the most immediate applications within procurement. It is a natural successor to robotic process automation (RPA) in the evolution of automated or autonomous procurement processes. While RPA is considered automated statistics, it lacks the ability to learn and improve over time.
Machine learning is also one of the most misunderstood aspects of AI in procurement organizations. Some enthusiasts consider any use of advanced statistical methods ML, while many software vendors portray human-like machines. It's time to dispel some myths by reviewing the core types of machine learning.

4 Machine Learning applications in procurement
Various machine learning techniques are used in procurement processes. Each machine learning type requires a varying degree of human intervention. The four types of machine learning include:
-
Supervised Learning: an algorithm is taught the patterns using past data, and then detects them automatically in new data. Supervision comes in the form of correct answers that humans provide to train the algorithm to seek out patterns in data. Commonly used within spend analysis in areas such as spend classification.
-
Unsupervised Learning: the algorithm is programmed to detect new and interesting patterns in completely new data. Without supervision, the algorithm is not expected to surface specific correct answers instead it looks for logical patterns within raw data. Rarely used within critical procurement functions.
-
Reinforcement Learning: the algorithm decides how to act in certain situations, and the behavior is rewarded or punished depending on the consequences. Largely theoretical in the procurement context.
-
Deep Learning: an advanced class of machine learning inspired by the human brain where artificial neural networks progressively improve their ability to perform a task. Emerging opportunity in procurement functions.
Machine Learning for Spend Analysis
Machine learning is already widely used across data-intensive processes such as procurement analytics. Let’s deep-dive into how machine learning is used in spend analytics and spend classification, and specifically to tackle the spend classification challenge.
Spend analysis is the process of identifying, collecting, cleansing, classifying, enriching, and analyzing your organization's spend data.
Spend Classification Problems and Challenges
Classifying spend into procurement categories is the key challenge in procurement spend analytics. Spend classification is among the earliest applications of artificial intelligence in procurement. AI is widely used today to automate classification.
Challenge 1: Spend categorization at scale
Procurement organizations face the need to categorize millions of unique transactions into procurement categories. Transaction data is coming from invoices, purchase orders or other data sources. Procurement organizations with good intentions create complex hierarchies of categories and sub-categories but often find it difficult to maintain a high data quality or efficiency in categorizing new data.
Challenge 2: Need for hyper-relevant, timely data
In the past, it was common that procurement spend was analyzed once a year or each quarter. Automation of processes enables shorter spend analysis cycle time. Today, high-performing Procurement organizations rely on nearly real-time data updates to meet the changing business needs.
Challenge 3: The amount of data is growing
Another key challenge is that the amount of data available is growing across different source systems. There is an increasing challenge to connect heterogeneous sources of data. Procurement organizations may need to bring together spend data from across a number of enterprise planning systems (ERPs), purchase-to-pay solutions or other finance-related software. Each source system may contain only some relevant data points, and there is a need to connect disparate spend data into one hierarchy.

Spend classification example: IT hardware
For example, a new computer may be labeled as IT equipment in the general ledger, while the invoice line description provides additional detail distinguishing it as a desktop computer. The purchase order for this item may even have a different description, referring to a vendor or maker-specific data points. While all these data sources refer to the same item, it requires intelligence to make a correct classification.
AI in Procurement Spend Classification
While various aspects of AI can help address or reduce the spend classification challenge, most software solutions today rely on supervised machine learning. Let's go through a concrete example of machine learning-powered spend classification.
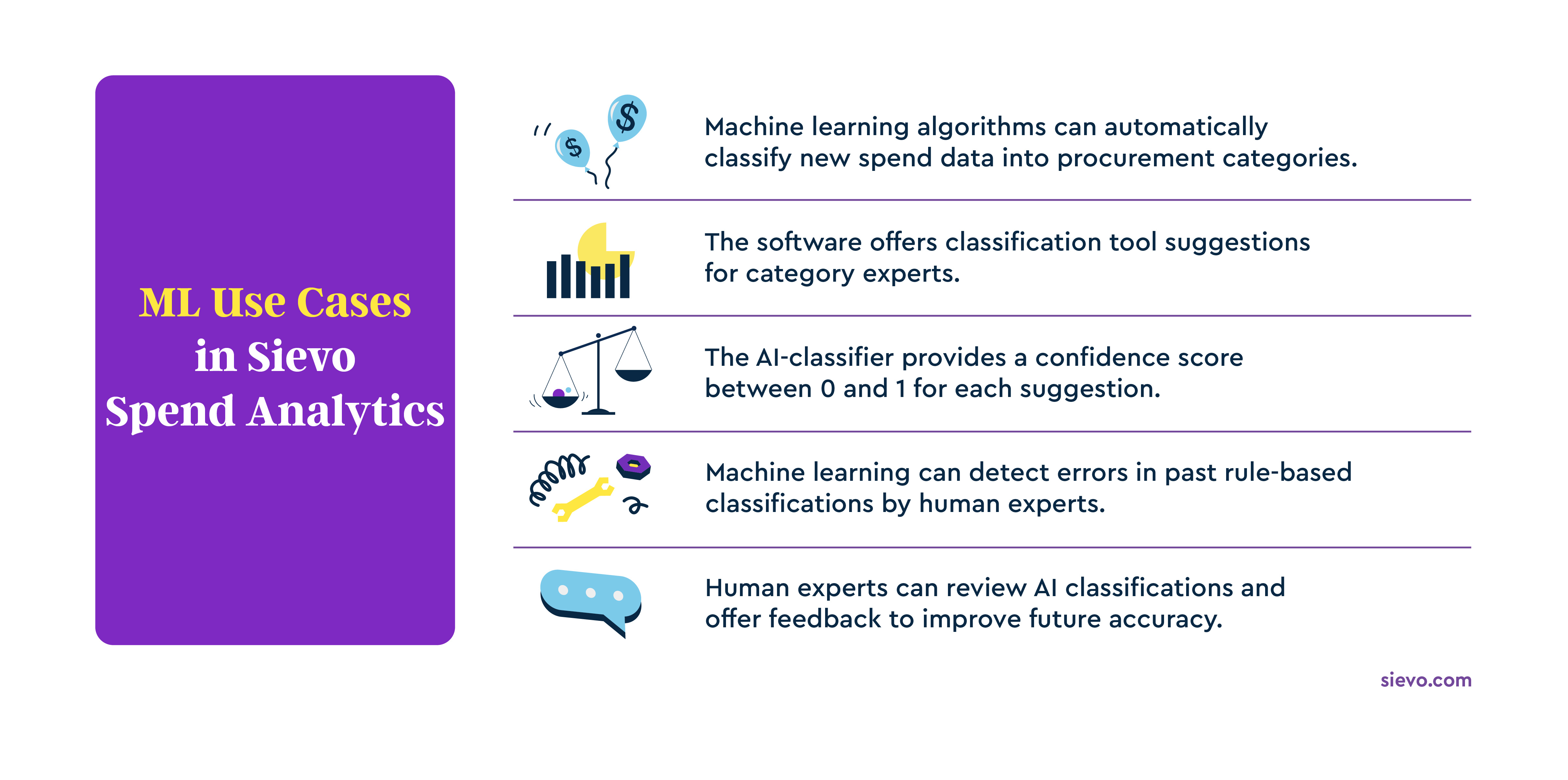
In a machine learning–powered spend classification workflow:
-
New spend data is automatically classified into procurement taxonomies based on learned patterns
-
Classification suggestions are provided to category experts through a review interface
-
Each suggestion includes a confidence score, typically ranging from 0 to 1, indicating the likelihood of correctness
Machine learning can also go beyond new spend classification. By analyzing historical data, it can identify errors in previous rule-based or manual classifications, improving overall data quality.
When category experts review and validate AI-classified data, their feedback becomes new training input. Over time, this feedback loop increases classification accuracy and reduces the need for manual intervention.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Procurement
Natural language processing (NLP) is the branch of artificial intelligence focused on understanding, interpreting, and manipulating human language. For procurement, NLP can uncover insights from existing data or streamline time-consuming processes. Let's go through some concrete examples. Data contained in legal contracts and documents can be parsed (interpreted) by AI for the procurement of relevant information.
NLP in Contract Management
Legal contracts contain valuable information for procurement, including termination dates, payment terms, and renegotiation rights. Historically, this information has not been readily accessible to procurement teams because contracts have been written in contractual terms and stored offline or in shared online folders, making the data contained in contracts difficult to access.
NLP enables procurement teams to extract this information through text parsing, allowing contract management software to:
-
Scan large volumes of contracts
-
Identify and extract key clauses and terms
-
Surface risks, obligations, and opportunities
In addition, optical character recognition (OCR) extends NLP capabilities by converting scanned or image-based contracts into machine-readable text, including previously non-digitized documents.
Word Embedding in Invoice Descriptions
Procurement data often includes free-text fields, such as invoice line descriptions or purchase order notes, which are difficult to analyze using traditional rules.
Word embedding is an NLP technique that represents words and phrases based on their similarity and context. In procurement, word embedding helps:
-
Interpret inconsistent or abbreviated descriptions
-
Group similar items across invoices and POs
-
Improve spend classification at the category and sub-category level
This allows procurement analytics systems to handle language variation more effectively.
Natural Language Generation in Chat Bots
Chatbots and personal assistants are among the most talked-about applications of AI that rely on natural language generation (NLG). These take NLP further by first interpreting human input and then giving a response in a written narrative. Voice-based assistants like Siri or Alexa are already widely used in consumer applications, but NLG is currently limited within procurement to pre-configured chatbots or virtual assistants that automate very limited tasks.
Cognitive Procurement Explained
Cognitive procurement is one of the most talked-about buzzwords. With new technologies and AI opportunities come new terms and definitions.

What is Cognitive Procurement?
Cognitive procurement is the process in which self-learning AI techniques are used to mimic human intelligence. These self-learning AI techniques include automated data mining, machine learning, pattern recognition, and NLP. The phrase "cognitive procurement" originates from an emerging field of advanced computer science, “cognitive computing.”
What is Cognitive Computing?
Cognitive Computing (CC) refers to any hardware or software that mimics the functioning of the human brain and helps improve decision-making. It models how the human brain senses, reasons, and responds to stimulation to solve specific tasks or challenges.
What is Cognitive Analytics?
One way in which cognitive computing can relate to Procurement is through cognitive analytics (CA). CA is a new approach to generating insights from large amounts of structured or unstructured data by mimicking a human brain’s ability to interpret patterns and draw conclusions from data. While many procurement analytics challenges may be solved by cognitive analytics, not every AI-assisted analytics solution involves cognitive solutions.
What is Cognitive Sourcing?
Another way that cognitive computing can support Procurement is by assisting sourcing processes. Cognitive sourcing can help buyers and Procurement teams to identify new opportunities or automate non-strategic sourcing activities. Sourcing assistants, such as chatbots, can be considered examples of cognitive sourcing.
Challenges with Cognitive Procurement
The field of cognitive computing is relatively new, so it should be approached with caution. There is not yet a broad consensus on core definitions and what constitutes “cognitive” processes in a business context. At the same time, many software solutions are being offered with the promise of embedded human-like intelligence. While technology is developing fast, it is recommended to validate assumptions within cognitive procurement with internal or external information systems experts.
Agentic AI in Procurement
Agentic AI is emerging as the next major step in the evolution of artificial intelligence, with significant implications for procurement. While traditional AI has focused on accelerating individual tasks, agentic AI introduces a goal-oriented approach that helps procurement teams move from analysis to action faster and more consistently.
Agentic AI is a more autonomous form of artificial intelligence designed to analyze data holistically, make context-aware recommendations, and take or coordinate actions when appropriate. Rather than responding only to user queries or producing static reports, agentic AI systems operate continuously against defined objectives.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is an autonomous form of artificial intelligence that proactively analyzes data, generates recommendations, and automates decision-making when appropriate. Unlike traditional AI and automation tools that focus on accelerating individual transactional tasks, Agentic AI is designed to continuously interpret data and act in alignment with defined objectives.
Its core value lies in reducing the gap between insight and execution by orchestrating decisions and processes rather than merely reporting on them.
Agentic AI has the potential to redefine procurement operations by reducing reliance on manual dashboards, integrating risk management more effectively, and making advanced analytics accessible without specialized AI or data science expertise.
Agentic AI Use Cases in Procurement
One practical example is reducing maverick spend. Agentic AI can continuously monitor purchasing behavior against procurement policies and respond automatically:
-
Enforcing procurement policies without manual intervention
-
Providing real-time guidance when purchases fall outside approved channels
-
Learning over time to better detect and prevent non-compliant patterns
AI Best Practices in Procurement
Start with boring problems
To start with AI, don't look for miraculous new solutions to change the way you run your Procurement operations. Don’t think of AI as a magical new technology. Instead, think of AI from the business process point of view. Consider the challenging yet routine business operations that already consume time and resources. The most immediate value of AI will not come from new applications, but from embedding technology into existing processes – for example, improving your existing spend analysis or contract management processes.
Capture all possible procurement data
Another general rule of thumb is to capture as much data relevant to Procurement as you can before you know how to use it. Don’t wait for your data quality to be perfect. Instead, assume that AI technologies can help you interpret and improve historic data quality over time. The key is to collect more data for AI to interpret. The more data you give AI to train on, the better results you're likely to get.
Give AI clear procurement challenges
In its current state, AI and machine learning are very good at narrow use cases. You can utilize machine learning to categorize Procurement costs based on invoice line items, but you're not likely to have AI take over complex supplier negotiations. Evaluate which routine tasks require a lot of your procurement team's time but have clear outcomes on performance.
Be open to experimenting
While AI has the potential to improve Procurement performance over time, there are still many uncertainties. Be open to experimenting. Consider giving emerging AI technology specialists challenges and training samples of your data. Allow for mistakes and learning, and focus on the expected business benefits. Recognize also that technology is developing at a fast pace, so failed experiments of tomorrow can be possible with the new AI methods of today.
Enable Human + Machine Collaboration
Finally, remember that all implementations of AI in Procurement will require active guidance and support from Procurement experts. Plan for human and machine collaboration, where your Procurement team’s expertise is augmented, not replaced, by artificial intelligence. Be the champion of change to make the best use of both human and machine intelligence.
Future of Procurement
No one can truly know where we will be in the next 10-20 years, but some conclusions can be drawn about what will be possible in the near future for AI and procurement. There is a strong consensus among the analyst community that applications already in use will continue to evolve.
It’s impossible to say with certainty where Procurement AI will take us in the end, but we made some predictions on what level of maturity AI could possibly achieve:
Total process automation: No human involvement will be required in operational procurement, including routine processes, approvals, compliance, and reporting.
Automated value creation: Machines may be able to make decisions and take action on savings and value generation opportunities without human input.
Full spend transparency: All procurement-related spend could be leveraged and available whenever key stakeholders need it – with no errors or faults.
Agile supplier ecosystems: Managing strategic supplier relationships will take on a new dimension as data flows freely between partner systems.
AI will provide recommendations and take actions based on data across the ecosystem, not just based on the data of a certain player. These are hypothetical scenarios, but they could be the possible culmination of the current AI applications.
The future of procurement depends on its ability to deliver measurable business value. Transformation of procurement aims to maximize procurement ROI (return on investment) in terms of:
-
cost savings,
-
efficiency,
-
collaboration,
-
innovation,
-
sustainability,
-
and financial success.

The procurement ROI is measured by comparing the procurement function’s costs with the cost savings it generates. These cost savings can further enable investments, research & development, improved customer experience, sales enablement, sustainable offering, and more. This is where AI can increase the impact of procurement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Popular questions about artificial intelligence among procurement professionals include the following.
What procurement use cases benefit most from AI?
AI delivers the most value in high-volume, repeatable, data-intensive procurement activities, including spend classification, supplier normalization, contract analysis, risk monitoring, anomaly detection, and recurring reporting.
Should organizations change their processes to accommodate AI, or should AI work with existing processes?
Capturing data early is one of the strongest foundations for long-term AI value. In most cases, AI can be applied directly to existing procurement processes. Organizations do not need to redesign workflows before they can start benefiting from AI. Modern AI tools are designed to work with current systems, data structures, and operating models.
The most effective way to prepare for AI value—both now and over the next three to five years—is to capture as much relevant data as possible, even if it cannot be fully processed or analyzed today. Large, accessible datasets create options. As AI capabilities improve, organizations may be able to extract value from historical and external data in ways that are not yet obvious.
What does AI governance look like? How do you govern machine learning?
AI governance in procurement typically revolves around how humans and machines collaborate in decision-making. There are three common governance models.
-
Human-in-the-loop means every AI-generated output is reviewed by a human before action is taken. This model is well-suited for high-risk, high-value, or low-volume decisions where accuracy and accountability are critical.
-
Human-on-the-loop means AI operates autonomously for routine tasks, while humans supervise the system and intervene only when needed. This approach works well for repetitive, high-volume processes such as classification, monitoring, or alerting.
-
Human-out-of-the-loop means AI systems operate without real-time human intervention. This model is rare in procurement and is typically used only in environments where speed is more important than human oversight, such as high-frequency trading.
How does AI improve spend analysis?
AI improves spend analysis by automating data cleansing, classification, enrichment, and error detection across multiple source systems. Machine learning improves classification accuracy over time through feedback and analysis of historical data.
How should procurement teams start using AI?
Procurement teams should start with routine, data-heavy problems already embedded in existing processes. Early success typically comes from improving spend analysis, contract visibility, or reporting rather than pursuing transformational use cases.
Does AI fully automate procurement processes?
No. Most real-world procurement AI deployments support partial automation rather than full autonomy. Routine, high-volume tasks can often be automated, while exceptions, low-confidence outputs, and high-impact decisions continue to require human review and approval. Agentic AI increases the level of autonomy by coordinating multi-step workflows and moving from insight to action, such as triggering reviews, escalating risks, or initiating predefined processes. Even so, agentic AI operates within human-defined guardrails, including approval thresholds, escalation rules, and audit requirements.
What Is Agentic AI in Procurement?
Agentic AI in procurement refers to artificial intelligence systems that can analyze data, reason across multiple inputs, and take or coordinate actions toward a defined goal, rather than supporting a single isolated task. Unlike traditional AI, which typically produces insights or recommendations for humans to act on, agentic AI is designed to bridge the gap between insight and execution within clearly defined rules and governance.
About Sievo
Sievo provides actionable procurement analytics based on data you can trust.
Designed for large enterprises with $1B+ in revenue, loved by global companies featuring Mars, Levi’s, and Deutsche Telekom, and praised by key analysts, we provide a future-proof solution with immediate ROI.
We empower Procurement, Finance, IT, and Sustainability teams to overcome their data chaos and capture all insights, drive bottom-line savings, improve ESG performance, and streamline budgeting and forecasting.
Sievo goes beyond world-class analytics and dashboards. We help our customers close the data-to-action gap with reliable insights, recommendations, and benchmarks by combining internal, third-party, and cross-customer data.
By processing spend data equivalent to 2% of the world's GDP annually, we enable fast, informed decision-making and deliver the industry's highest data quality with end-to-end data accountability.
Awarded and recognized by top analysts including Spend Matters, ProcureTech, and Procurement Leaders – we offer solutions for Spend Analytics, Procurement Performance Measurement, ESG Analytics, and Financial Planning and Analysis.
We call it procurement excellence - but you can call it Sievo.